XM™|How to open the FX account.
XM offers an execution combination of "Exchange marry" where buy/sell orders from clients are matched with each other for each currency pair and a system where client order can meet the best rate among the liquidity from multiple providers, as a result, XM can provide stable trading environment. XM, one of the leading FX brokerage houses, has enormous numbers of orders from traders matched and is proud of its execution ratio (execution power) and execution speed which overwhelms competitors.
All the orders are executed through NDD (No Dealing System) which is without the human intervention by dealers with XM. For that reason, XM can realize and provide fair trading environment which does not cause the execution against interest of clients.
![]()
"Execution ratio" or "Execution power" which is the potential power of FX brokerage houses on placing orders is becoming focused in these days. Recently there are more traders who select brokerage house depending on its execution power than the narrowness of the spread or the fee amount among the traders using overseas FX brokerage houses. Then what does "Execution ratio/Execution power" on concluding the orders from traders mean and why do many traders put a stress on execution? Here are the explanations with specific examples.
When you select currency pair in FX trading and place an order, there should be a time lag between placing an order and execution/response. Execution ratio is generally worked out by splitting the time lag with certain duration (second) and show the ratio of order execution in per cent.
How many per cent of orders are executed within the time lag (xx seconds) equal execution ratio
When this execution ratio is a high number, which is, if the system obtains a number close to 100%, execution ratio is regarded as high (and excellent) and the ratio is low, the execution ratio is regarded as low.
Suppose a trader tries to close the long position at a rate of 99.90 (meaning place a sell order). If his/her order is filled at point A, execution rate is 99.90, however if his order is filled at point B, his/her order is filled at 99.80. As the result of that, it will end up with the loss.
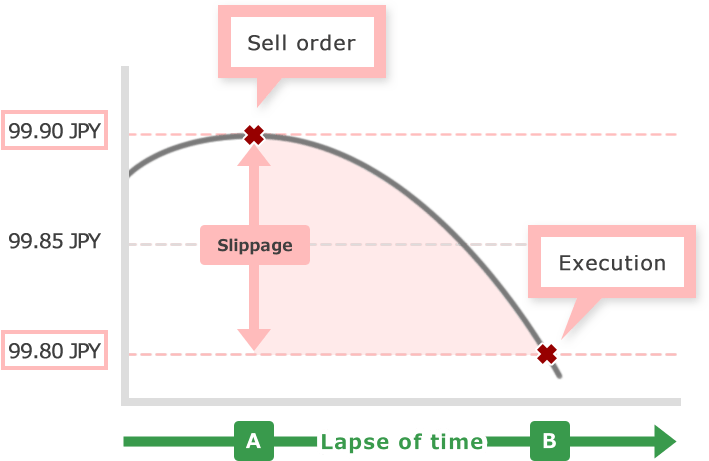
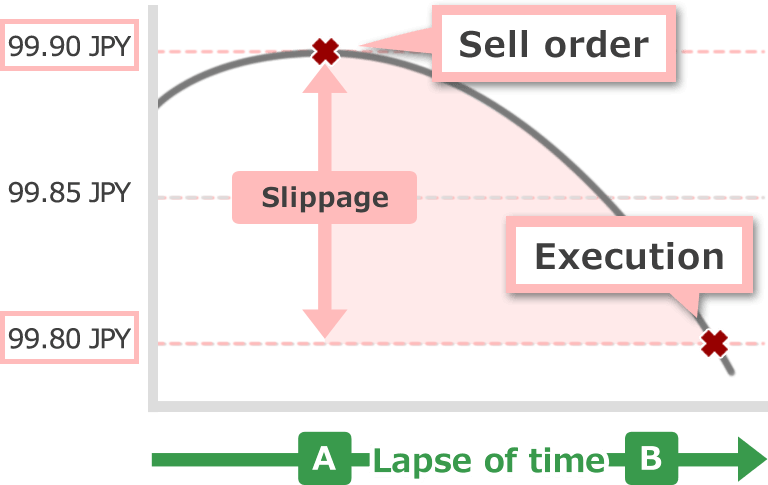
These cases can be seen significantly in volatile markets or markets with big movement. Gap between order prices (indices) you specified and prices executed is likely to occur with the brokerage houses which does not have a strong execution power and you cannot trade as you want. This gap is called slippage (or also called "slipping.")
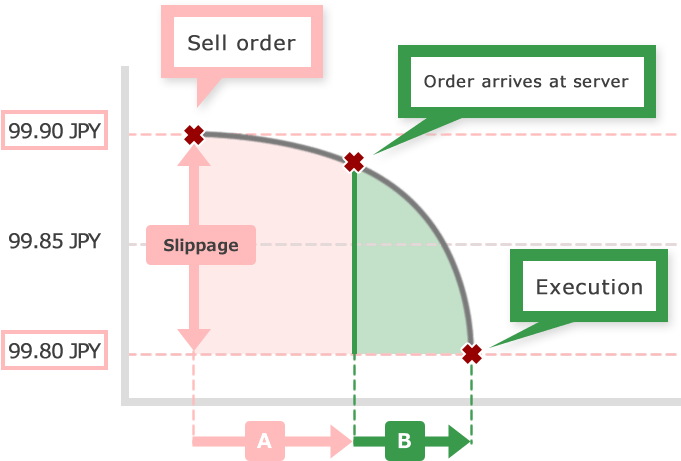
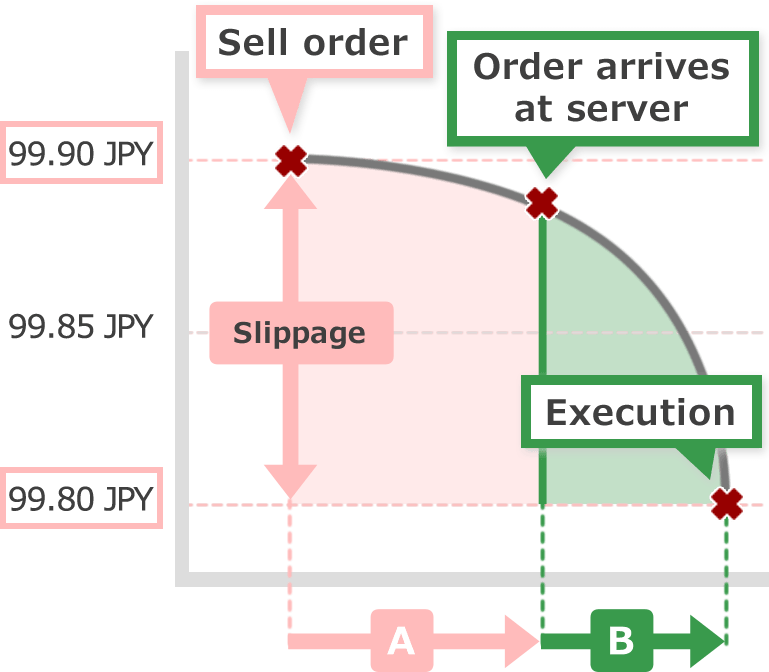
Slippage, the gap between order prices you specified and prices executed could occur from two factors.
One is the factor arising from internet connection between user and brokerage house or infrastructure. Internet connection speed at client's home or physical problem at data center of the brokerage house is the main cause. (See 【A】 of the figure)
The other is arising from the system how FX brokerage house receive orders and liquidity. FX market moves 24 hours and buy/sell rates changes in a moment. That is why FX brokerage houses usually cover their position coming from each trader in some way. FX brokerage houses which have many covering counterparty (liquidity provider) tend to execute the orders at a better price and at a rapid speed, on the other hand, FX brokerage houses which do not have many liquidity providers tend to require more time or fail to execute due to few choices. (See 【B】 of the figure)
Here is the further explanation of the two factors of slippage.
A
Being the trading through internet connection, FX trading is affected by the internet environment used at the time of order placement to no small extent. However the effect on slippage should be less as far as clients access brokerage house from internet environment at clients' home or office inside Japan. Especially in Japan, where usage ratio of smartphone is more than 85%, slippage arising from internet environment almost does not occur as far as connection is through 3G or 4G.
When trading robots by expert advisers are used, operation time tend to become longer and operating environment of hardware for expert advisers have an effect on trades, as a result, more traders are using VPS (virtual private service) than before. Especially when high speed and high frequency trading (a high speed, high frequency and repeated trading procedure and method programmed) is deployed, which is called HFT, use of VPS is essential as the physical positional relation between trading server and VPS is also important.
When VPS is used, MetaTrader will be operated on stable internet connection by the data center and through the managed Windows server, that is why there is a higher effect of slippage not occurring due to access environment.
With XM VPS environment is available which locates 1.5 km away from XM data center in London and is connected through light fiber. If trade is through XM's VPS, EA operation does not have to be supervised through each PC and non-stop trading can be realized within the stable environment. XM's VPS service gives you access to 1.5GB RAM, 20GB hard drive capacity and Windows 2012 server backed up by a stable CPU power source of 600 MHz.

See here for XM's VPS service for further explanation
B
Normally FX brokerage houses decide whether they offset orders by themselves inside or place orders to counterparties when they receive orders from clients. If a brokerage house decides offset orders inside itself, for example, a "client A" place an order to buys dollars at a rate of 109 and another sells dollars at the same rate, then the brokerage house can offset these two orders by itself without the risk as far as the market does not move. The operation where orders are offset within the house is called exchange marry.
Exchange marry is useful when FX market is stable and does not have a big movement, however FX market always moves and there are various orders from clients. When FX brokerage houses decide that they cannot keep their position in a particular currency pair square (balanced), they try to counter-trade in FX market or with liquidity provider, and keep their position square and avoid FX fluctuation risk. This is called cover deal.
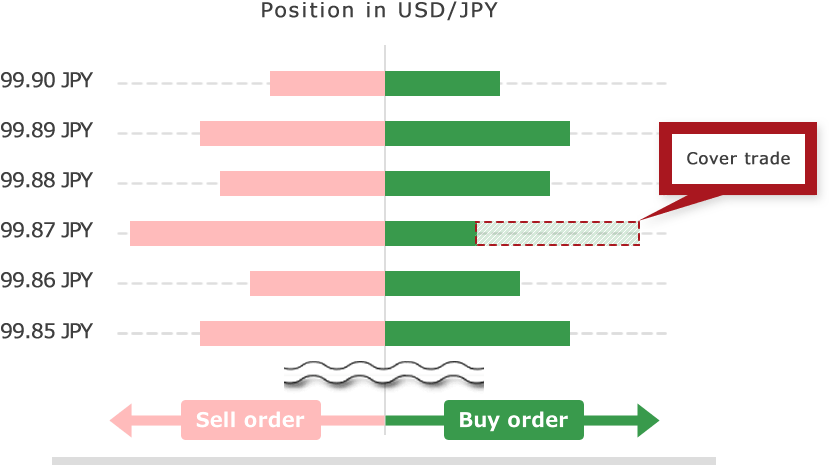
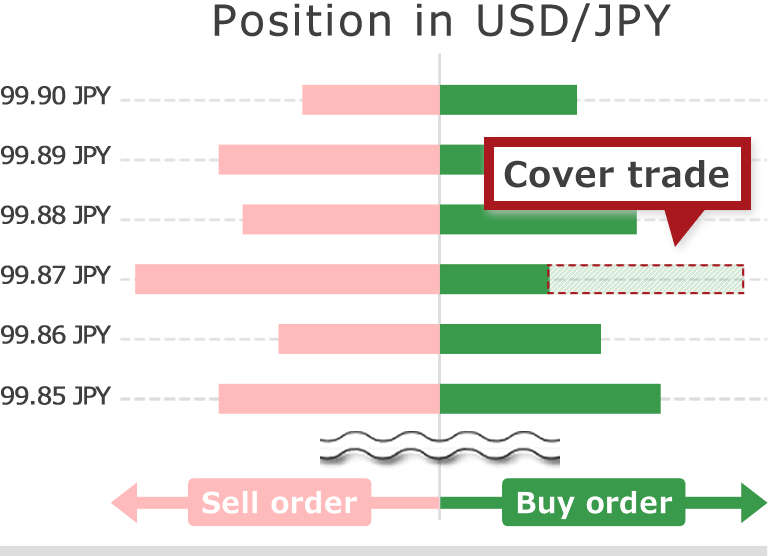
Generally FX brokerage houses who use exchange marry as their order system are called B-book brokerage houses and FX brokerage houses who use cover deal are called A-book brokerage houses. STP (straight through processing) which is often mentioned as the feature of brokerage house is a type of cover deal.
Slippage basically does not occur in exchange marry. This is because brokerage houses accept orders first and place orders which excesses square position (balanced) within the brokerage house to the covering counterparty, and there is no room for execution rejection or slippage. However execution rejection or slippage can occur with B-book brokerage houses. This depends on the order volume they accept and liquidity of the covering counterparty.
Exchange marry is logically a system where brokerage houses receive all the orders when clients place orders. However if risk of FX movement is too big, brokerage houses cannot take all the risk. If there is an abnormally big order where brokerage houses cannot keep the position square or minor currency pairs which brokerage houses cannot find sufficient number of covering counterparties, there may be the cases where brokerage houses reject the orders (also called requote.)
When brokerage houses cover deal, they are greatly affected through the liquidity of the covering counterparty. When brokerage houses cover deal, it is more likely that they use prime brokers which deal with bigger amount or financial institutions than FX brokerage houses themselves. So it is dependent if their orders are accepted on the liquidity of the covering counterparty. For example, if "client A" uses a brokerage house" brokerage house A" who is a A-book brokerage house, execution power depends on which covering counterparty the brokerage house A ties up and places orders with. This really affects slippage.
For covering counterparty "Brokerage House A" is also one of the clients, therefore covering counterparty also takes margin money (collateral), then the brokerage house can trade with the counterparty. That is why not only the liquidity of the covering counterparty but also if the brokerage house is in a situation to be able to give orders is an important factor.
Discussion which is favorable, "A-book brokerage house" which mainly uses cover deal as its main order system or "B-book brokerage house" which uses exchange marry as its main order system has been long-lasting, however both have merits and demerits.
Generally it is said that "A-book brokerage house is favorable as it has high transparency, there is no conflict of interest and fraudulent operation, however there are many cases that the parent company of A-book brokerage house itself is an investment company or a financial institution. So if the covering counterparty is any of the group company, can we easily say that it is a transparent trade? And in case of STP/instant execution slippages and execution rejections tend to happen often and the stability of trade itself is becoming very low. In addition to it, brokerage houses which deal with only with A-book brokerage houses cannot penetrate into the high leverage market (1:200 to 1:500/1,000.) Because the highest leverage ratio of the covering brokerage house should be about 1:100.
On the other hand it is said that "B-book brokerage houses are likely to be more fraudulent than A-book due to conflict of interest," however exchange marry basically needs numbers of orders from many clients in order to realize exchange marry. Therefore only brokerage houses which are big and have many client base can deal with exchange marry. Adding to it, B-book brokerage houses do not depend on the covering counterparty, they are not dependent on covering counterparty and can maintain stable trade environment not dependent on the market.
Problem lies in the B-book brokerage houses which are not big enough to be able to deal with exchange marry. As discussed earlier, exchange marry needs many orders. Therefore newly-entering FX brokerage houses cannot create a system where they can physically offset the position within themselves and keep their position flat. As a result, these brokerage houses have more positions they cannot marry by themselves and put themselves into the position where they only wish that clients fail in that trade. These brokerage houses are in a position where they are in a conflict of interest with clients and they may end up with not executing a particular position, have the slippage occur intentionally and have the order executed in the brokerage houses' favorable position or get themselves involved in a wrongful act.
XM mainly uses exchange marry as a B-book brokerage house. However XM's feature among others is its enormous numbers of orders from clients compared with competitors. That is why XM can keep almost all the orders square (balanced) within the house and the ratio of cover deal is significantly low.
Adding to it, XM eliminates human intervention from dealing desk in order to overcome the doubt of conflict of interest to clients. By doing this, XM successfully preclude the control of position targeting individual client or specific trade and all the acts that cause doubts of intervention to the trade.
With this innovation clients can use highly fair and transparent hybrid order system which is the combination of A/B order system and XM is proud of. XM achieved 99.98% of average execution ratio per second in 2017 and has been renewing the top record among FX brokerage houses since then.
Dealers take care of clients' orders in ordinary FX brokerage houses which deploy ordinary dealing system. Dealers normally place same kind of orders to the counterparty such as banks (cover deal) and make money from the difference (spread) between the order from the client and the price they cover at the covering counterparty. Therefore if the dealers in the house cannot find the rate they can obtain profit, they may requote the price and show an unfavorable price for the client.
If dealers decide not to place clients' orders to counterparties such as banks, and clients suffer a loss, it will become a gain for the FX brokerage house and vice versa. Traders may not be able to trade at ease. Is this situation allowed?
XMTrading (XM)'s next generation NDD system is the state-of-the art order system excluding human intervention at all. All the orders are dealt without the decision of dealers and processed automatically through our system inside.
XM's fair price indication and speedy execution is praised as world No. 1. Clients can enjoy trading at ease where there is no rejection of the trade and no requote.
NDD (No Dealing Desk) system which XM deploys is the order system where orders are executed without human intervention. All the orders are automatically executed without the intervention of dealers. Therefore XM realizes fair trading environment which does not cause the conflict of interest to the clients.
2021.09.02
Why high execution power realized with XM?
XM puts more emphasis on exchange marry backed by the enormous numbers of clients and their orders than cover deal. By doing this, XM can avoid delay of execution or lack of liquidity which is the weak point of cover deal and achieve high execution environment.
2021.09.02
How high is the execution power of XM?
XM's average execution ratio is 99.98% and top level execution power among the competitors is achieved. Execution ratio or power is the probability where orders are executed as clients intend. Closer the ratio to 100%, execution power is high, and lower the ratio, execution power is low.
2021.09.02
What kind of order system is used with XM?
XM deploys A/B hybrid system which combines exchange marry matching clients' orders with each other and cover deal with multiple partner counterparties. XM also deploys NDD (No Dealing Desk) system where these orders are executed without human intervention.
2021.09.02
Does order system differ depending on account types?
No, XM uses the same order system for all the accounts. In all the account types such as Micro Account and Standard Account the A/B Hybrid order system for NDD (No-dealing system) is deployed.
2021.09.02